|
The Acceleration Analysis calculates the acceleration of the selected points and graphs them over time.
The following formula is used to calculate the acceleration:
Velocity Frame n - Velocity Frame n-DerivativeLength / Time Frame n - Frame n - DerivativeLength
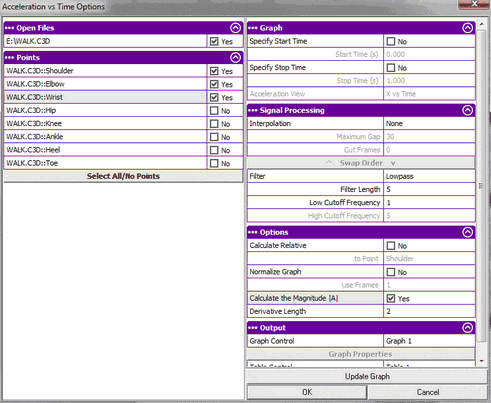
Acceleration Analysis Options
|
Calculate Relative
|
This will subtract the motion of the selected point, i.e. translate the motion to selected point.
|
Normalize Graph
|
This will calculate the average of the specified number of frames starting with frame 1 and then subtract this from every frame. This will result in the change of motion instead of absolute motion.
|
Calculate the Magnitude |A|
|
This will calculate the sqrt( x2 + y2 + z2 ) or sqrt( x2 + y2 ) in case of 2D of the acceleration.
|
Derivative Length
|
This is the number of frames that the derivative will skip over in order to create a smoothing effect. The default is 2 meaning it will use every other frame.
|
|